版本 0.20.1 (2017年5月5日)#
这是从 0.19.2 版本以来的一个主要发行版,包含了大量的 API 更改、弃用、新功能、增强和性能改进,以及大量的错误修复。我们建议所有用户升级到此版本。
主要亮点包括
Series/DataFrame 新增
.agg()API,类似于 groupby-rolling-resample API,详见 此处与
feather-format集成,包括新的顶层pd.read_feather()和DataFrame.to_feather()方法,详见 此处。.ix索引器已被弃用,详见 此处Panel已被弃用,详见 此处添加了
IntervalIndex和Interval标量类型,详见 此处在
.groupby()中按索引级别分组时,改进了用户 API,详见 此处改进了对
UInt64dtype 的支持,详见 此处JSON 序列化的新 orient,
orient='table',它使用 Table Schema 规范,并使得在 Jupyter Notebook 中提供更具交互性的 repr 成为可能,详见 此处实验性支持将带样式的数据帧 (
DataFrame.style) 导出到 Excel,详见 此处窗口二元 corr/cov 操作现在返回一个 MultiIndexed
DataFrame而不是Panel,因为Panel现已弃用,详见 此处S3 处理现在使用
s3fs,详见 此处Google BigQuery 支持现在使用
pandas-gbq库,详见 此处
警告
pandas 已更改代码库的内部结构和布局。这可能会影响非顶层 pandas.* 命名空间中的导入,请查看 此处 的更改。
注意
这是 0.20.0 和 0.20.1 版本的合并发布。版本 0.20.1 包含一个额外的更改,用于向下兼容使用 pandas utils 例程的下游项目。(GH 16250)
v0.20.0 版本新特性
新功能#
DataFrame/Series 的 agg 方法 API#
Series 和 DataFrame 已增强以支持聚合 API。这是一个来自 groupby、窗口操作和重采样的熟悉 API。这允许通过使用 agg() 和 transform() 以简洁的方式进行聚合操作。完整文档见 此处 (GH 1623)。
以下是一个示例
In [1]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randn(10, 3), columns=['A', 'B', 'C'],
...: index=pd.date_range('1/1/2000', periods=10))
...:
In [2]: df.iloc[3:7] = np.nan
In [3]: df
Out[3]:
A B C
2000-01-01 0.469112 -0.282863 -1.509059
2000-01-02 -1.135632 1.212112 -0.173215
2000-01-03 0.119209 -1.044236 -0.861849
2000-01-04 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-05 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-06 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-07 NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-08 0.113648 -1.478427 0.524988
2000-01-09 0.404705 0.577046 -1.715002
2000-01-10 -1.039268 -0.370647 -1.157892
[10 rows x 3 columns]
可以使用字符串函数名、可调用对象、列表或这些的字典进行操作。
使用单个函数等同于 .apply。
In [4]: df.agg('sum')
Out[4]:
A -1.068226
B -1.387015
C -4.892029
Length: 3, dtype: float64
使用函数列表进行多次聚合。
In [5]: df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
Out[5]:
A B C
sum -1.068226 -1.387015 -4.892029
min -1.135632 -1.478427 -1.715002
[2 rows x 3 columns]
使用字典可以为每列应用特定的聚合器。您将获得所有聚合器组成的矩阵式输出。输出中每列对应一个唯一函数。那些应用于特定列的函数将是 NaN
In [6]: df.agg({'A': ['sum', 'min'], 'B': ['min', 'max']})
Out[6]:
A B
sum -1.068226 NaN
min -1.135632 -1.478427
max NaN 1.212112
[3 rows x 2 columns]
API 还支持一个用于广播结果的 .transform() 函数。
In [7]: df.transform(['abs', lambda x: x - x.min()])
Out[7]:
A B C
abs <lambda> abs <lambda> abs <lambda>
2000-01-01 0.469112 1.604745 0.282863 1.195563 1.509059 0.205944
2000-01-02 1.135632 0.000000 1.212112 2.690539 0.173215 1.541787
2000-01-03 0.119209 1.254841 1.044236 0.434191 0.861849 0.853153
2000-01-04 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-05 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-06 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-07 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN
2000-01-08 0.113648 1.249281 1.478427 0.000000 0.524988 2.239990
2000-01-09 0.404705 1.540338 0.577046 2.055473 1.715002 0.000000
2000-01-10 1.039268 0.096364 0.370647 1.107780 1.157892 0.557110
[10 rows x 6 columns]
当遇到无法聚合的混合 dtype 时,.agg() 只会执行有效的聚合。这类似于 groupby .agg() 的工作方式。(GH 15015)
In [8]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3],
...: 'B': [1., 2., 3.],
...: 'C': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'],
...: 'D': pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3)})
...:
In [9]: df.dtypes
Out[9]:
A int64
B float64
C object
D datetime64[ns]
Length: 4, dtype: object
In [10]: df.agg(['min', 'sum'])
Out[10]:
A B C D
min 1 1.0 bar 2013-01-01
sum 6 6.0 foobarbaz NaT
数据 IO 的关键字参数 dtype#
read_csv() 的 'python' 引擎,以及用于解析固定宽度文本文件的 read_fwf() 函数和用于解析 Excel 文件的 read_excel() 函数现在都接受 dtype 关键字参数,用于指定特定列的类型 (GH 14295)。有关更多信息,请参阅 IO 文档。
In [10]: data = "a b\n1 2\n3 4"
In [11]: pd.read_fwf(StringIO(data)).dtypes
Out[11]:
a int64
b int64
Length: 2, dtype: object
In [12]: pd.read_fwf(StringIO(data), dtype={'a': 'float64', 'b': 'object'}).dtypes
Out[12]:
a float64
b object
Length: 2, dtype: object
.to_datetime() 方法新增 origin 参数#
to_datetime() 新增了一个参数 origin,用于在解析具有特定 unit 的数值时,定义一个参考日期以计算结果时间戳。(GH 11276, GH 11745)
例如,以 1960-01-01 作为起始日期
In [13]: pd.to_datetime([1, 2, 3], unit='D', origin=pd.Timestamp('1960-01-01'))
Out[13]: DatetimeIndex(['1960-01-02', '1960-01-03', '1960-01-04'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
默认设置为 origin='unix',默认为 1970-01-01 00:00:00,通常称为“Unix 纪元”或 POSIX 时间。这是之前的默认设置,因此这是一个向后兼容的更改。
In [14]: pd.to_datetime([1, 2, 3], unit='D')
Out[14]: DatetimeIndex(['1970-01-02', '1970-01-03', '1970-01-04'], dtype='datetime64[ns]', freq=None)
GroupBy 增强功能#
传递给 DataFrame.groupby() 的字符串作为 by 参数,现在可以引用列名或索引级别名称。以前,只能引用列名。这允许同时按列和索引级别轻松分组。(GH 5677)
In [15]: arrays = [['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz', 'foo', 'foo', 'qux', 'qux'],
....: ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]
....:
In [16]: index = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=['first', 'second'])
In [17]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3],
....: 'B': np.arange(8)},
....: index=index)
....:
In [18]: df
Out[18]:
A B
first second
bar one 1 0
two 1 1
baz one 1 2
two 1 3
foo one 2 4
two 2 5
qux one 3 6
two 3 7
[8 rows x 2 columns]
In [19]: df.groupby(['second', 'A']).sum()
Out[19]:
B
second A
one 1 2
2 4
3 6
two 1 4
2 5
3 7
[6 rows x 1 columns]
read_csv 中对压缩 URL 的更好支持#
压缩代码进行了重构 (GH 12688)。因此,在 read_csv() 或 read_table() 中从 URL 读取数据帧现在支持额外的压缩方法:xz、bz2 和 zip (GH 14570)。以前只支持 gzip 压缩。默认情况下,URL 和路径的压缩现在通过其文件扩展名推断。此外,Python 2 C 引擎中对 bz2 压缩的支持也得到了改进 (GH 14874)。
In [20]: url = ('https://github.com/{repo}/raw/{branch}/{path}'
....: .format(repo='pandas-dev/pandas',
....: branch='main',
....: path='pandas/tests/io/parser/data/salaries.csv.bz2'))
....:
# default, infer compression
In [21]: df = pd.read_csv(url, sep='\t', compression='infer')
# explicitly specify compression
In [22]: df = pd.read_csv(url, sep='\t', compression='bz2')
In [23]: df.head(2)
Out[23]:
S X E M
0 13876 1 1 1
1 11608 1 3 0
[2 rows x 4 columns]
Pickle 文件 IO 现在支持压缩#
read_pickle()、DataFrame.to_pickle() 和 Series.to_pickle() 现在可以从压缩的 pickle 文件读写。压缩方法可以是显式参数,也可以从文件扩展名推断。请参阅 此处文档。
In [24]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': np.random.randn(1000),
....: 'B': 'foo',
....: 'C': pd.date_range('20130101', periods=1000, freq='s')})
....:
使用显式压缩类型
In [25]: df.to_pickle("data.pkl.compress", compression="gzip")
In [26]: rt = pd.read_pickle("data.pkl.compress", compression="gzip")
In [27]: rt.head()
Out[27]:
A B C
0 -1.344312 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:00
1 0.844885 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:01
2 1.075770 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:02
3 -0.109050 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:03
4 1.643563 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:04
[5 rows x 3 columns]
默认是从扩展名推断压缩类型 (compression='infer')
In [28]: df.to_pickle("data.pkl.gz")
In [29]: rt = pd.read_pickle("data.pkl.gz")
In [30]: rt.head()
Out[30]:
A B C
0 -1.344312 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:00
1 0.844885 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:01
2 1.075770 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:02
3 -0.109050 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:03
4 1.643563 foo 2013-01-01 00:00:04
[5 rows x 3 columns]
In [31]: df["A"].to_pickle("s1.pkl.bz2")
In [32]: rt = pd.read_pickle("s1.pkl.bz2")
In [33]: rt.head()
Out[33]:
0 -1.344312
1 0.844885
2 1.075770
3 -0.109050
4 1.643563
Name: A, Length: 5, dtype: float64
UInt64 支持改进#
pandas 显著改进了对涉及无符号(或纯非负)整数操作的支持。此前,处理这些整数会导致不正确的舍入或数据类型转换,从而导致错误结果。值得注意的是,已创建了一个新的数值索引 UInt64Index (GH 14937)。
In [1]: idx = pd.UInt64Index([1, 2, 3])
In [2]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['a', 'b', 'c']}, index=idx)
In [3]: df.index
Out[3]: UInt64Index([1, 2, 3], dtype='uint64')
将类数组对象的对象元素转换为无符号 64 位整数时出现的 Bug (GH 4471, GH 14982)
Series.unique()中无符号 64 位整数导致溢出的 Bug (GH 14721)DataFrame构造中无符号 64 位整数元素被转换为对象的 Bug (GH 14881)pd.read_csv()中无符号 64 位整数元素被不正确转换为错误数据类型的 Bug (GH 14983)pd.unique()中无符号 64 位整数导致溢出的 Bug (GH 14915)pd.value_counts()中无符号 64 位整数在输出中被错误截断的 Bug (GH 14934)
对分类数据的 GroupBy#
在之前的版本中,当对数据中未出现的分类序列进行分组时,.groupby(..., sort=False) 会因 ValueError 而失败。(GH 13179)
In [34]: chromosomes = np.r_[np.arange(1, 23).astype(str), ['X', 'Y']]
In [35]: df = pd.DataFrame({
....: 'A': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'B': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'C': np.random.randint(100),
....: 'chromosomes': pd.Categorical(np.random.choice(chromosomes, 100),
....: categories=chromosomes,
....: ordered=True)})
....:
In [36]: df
Out[36]:
A B C chromosomes
0 87 22 81 4
1 87 22 81 13
2 87 22 81 22
3 87 22 81 2
4 87 22 81 6
.. .. .. .. ...
95 87 22 81 8
96 87 22 81 11
97 87 22 81 X
98 87 22 81 1
99 87 22 81 19
[100 rows x 4 columns]
之前的行为:
In [3]: df[df.chromosomes != '1'].groupby('chromosomes', observed=False, sort=False).sum()
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
ValueError: items in new_categories are not the same as in old categories
新行为:
In [37]: df[df.chromosomes != '1'].groupby('chromosomes', observed=False, sort=False).sum()
Out[37]:
A B C
chromosomes
4 348 88 324
13 261 66 243
22 348 88 324
2 348 88 324
6 174 44 162
... ... .. ...
3 348 88 324
11 348 88 324
19 174 44 162
1 0 0 0
21 0 0 0
[24 rows x 3 columns]
表格 schema 输出#
DataFrame.to_json() 的新 orient 'table' 将生成符合 Table Schema 的数据字符串表示。
In [38]: df = pd.DataFrame(
....: {'A': [1, 2, 3],
....: 'B': ['a', 'b', 'c'],
....: 'C': pd.date_range('2016-01-01', freq='d', periods=3)},
....: index=pd.Index(range(3), name='idx'))
....:
In [39]: df
Out[39]:
A B C
idx
0 1 a 2016-01-01
1 2 b 2016-01-02
2 3 c 2016-01-03
[3 rows x 3 columns]
In [40]: df.to_json(orient='table')
Out[40]: '{"schema":{"fields":[{"name":"idx","type":"integer"},{"name":"A","type":"integer"},{"name":"B","type":"string"},{"name":"C","type":"datetime"}],"primaryKey":["idx"],"pandas_version":"1.4.0"},"data":[{"idx":0,"A":1,"B":"a","C":"2016-01-01T00:00:00.000"},{"idx":1,"A":2,"B":"b","C":"2016-01-02T00:00:00.000"},{"idx":2,"A":3,"B":"c","C":"2016-01-03T00:00:00.000"}]}'
有关更多信息,请参阅 IO: Table Schema。
此外,如果您使用 IPython(或使用 Jupyter 消息协议的其他前端,如 nteract),DataFrame 和 Series 的 repr 现在可以发布 Series 或 DataFrame 的 JSON 表模式表示。这使得 Jupyter notebook 和 nteract 等前端在显示 pandas 对象时具有更大的灵活性,因为它们拥有更多关于数据的信息。您必须通过将 display.html.table_schema 选项设置为 True 来启用此功能。
从/到 SparseDataFrame 的 SciPy 稀疏矩阵#
pandas 现在支持直接从 scipy.sparse.spmatrix 实例创建稀疏数据帧。有关更多信息,请参阅 文档。(GH 4343)
支持所有稀疏格式,但如果矩阵不是 COOrdinate 格式,则会进行转换,并根据需要复制数据。
from scipy.sparse import csr_matrix
arr = np.random.random(size=(1000, 5))
arr[arr < .9] = 0
sp_arr = csr_matrix(arr)
sp_arr
sdf = pd.SparseDataFrame(sp_arr)
sdf
要将 SparseDataFrame 转换回 COO 格式的稀疏 SciPy 矩阵,您可以使用
sdf.to_coo()
带样式 DataFrames 的 Excel 输出#
已添加实验性支持,允许使用 openpyxl 引擎将 DataFrame.style 格式导出到 Excel。(GH 15530)
例如,运行以下代码后,styled.xlsx 呈现如下
In [41]: np.random.seed(24)
In [42]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': np.linspace(1, 10, 10)})
In [43]: df = pd.concat([df, pd.DataFrame(np.random.RandomState(24).randn(10, 4),
....: columns=list('BCDE'))],
....: axis=1)
....:
In [44]: df.iloc[0, 2] = np.nan
In [45]: df
Out[45]:
A B C D E
0 1.0 1.329212 NaN -0.316280 -0.990810
1 2.0 -1.070816 -1.438713 0.564417 0.295722
2 3.0 -1.626404 0.219565 0.678805 1.889273
3 4.0 0.961538 0.104011 -0.481165 0.850229
4 5.0 1.453425 1.057737 0.165562 0.515018
5 6.0 -1.336936 0.562861 1.392855 -0.063328
6 7.0 0.121668 1.207603 -0.002040 1.627796
7 8.0 0.354493 1.037528 -0.385684 0.519818
8 9.0 1.686583 -1.325963 1.428984 -2.089354
9 10.0 -0.129820 0.631523 -0.586538 0.290720
[10 rows x 5 columns]
In [46]: styled = (df.style
....: .applymap(lambda val: 'color:red;' if val < 0 else 'color:black;')
....: .highlight_max())
....:
In [47]: styled.to_excel('styled.xlsx', engine='openpyxl')
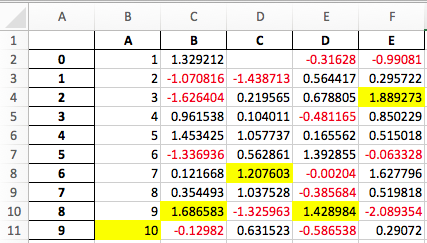
有关更多详细信息,请参阅 样式文档。
IntervalIndex#
pandas 获得了一个 IntervalIndex 及其自己的 dtype interval,以及 Interval 标量类型。这些使得区间表示法得到一流支持,特别是作为 cut() 和 qcut() 中类别的返回类型。IntervalIndex 允许一些独特的索引,请参阅 文档。(GH 7640, GH 8625)
警告
IntervalIndex 的这些索引行为是暂定的,可能会在未来的 pandas 版本中更改。欢迎提供使用反馈。
之前的行为
返回的类别是字符串,表示区间
In [1]: c = pd.cut(range(4), bins=2)
In [2]: c
Out[2]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3], (1.5, 3]]
Categories (2, object): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3]]
In [3]: c.categories
Out[3]: Index(['(-0.003, 1.5]', '(1.5, 3]'], dtype='object')
新行为
In [48]: c = pd.cut(range(4), bins=2)
In [49]: c
Out[49]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0], (1.5, 3.0]]
Categories (2, interval[float64, right]): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3.0]]
In [50]: c.categories
Out[50]: IntervalIndex([(-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0]], dtype='interval[float64, right]')
此外,这允许使用相同的 bin 来分箱*其他*数据,其中 NaN 表示缺失值,类似于其他 dtype。
In [51]: pd.cut([0, 3, 5, 1], bins=c.categories)
Out[51]:
[(-0.003, 1.5], (1.5, 3.0], NaN, (-0.003, 1.5]]
Categories (2, interval[float64, right]): [(-0.003, 1.5] < (1.5, 3.0]]
一个 IntervalIndex 也可以用作 Series 和 DataFrame 的索引。
In [52]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': range(4),
....: 'B': pd.cut([0, 3, 1, 1], bins=c.categories)
....: }).set_index('B')
....:
In [53]: df
Out[53]:
A
B
(-0.003, 1.5] 0
(1.5, 3.0] 1
(-0.003, 1.5] 2
(-0.003, 1.5] 3
[4 rows x 1 columns]
通过特定区间进行选择
In [54]: df.loc[pd.Interval(1.5, 3.0)]
Out[54]:
A 1
Name: (1.5, 3.0], Length: 1, dtype: int64
通过包含在区间内的标量值进行选择。
In [55]: df.loc[0]
Out[55]:
A
B
(-0.003, 1.5] 0
(-0.003, 1.5] 2
(-0.003, 1.5] 3
[3 rows x 1 columns]
其他增强功能#
DataFrame.rolling()现在接受参数closed='right'|'left'|'both'|'neither'来选择滚动窗口的闭合性。详见 文档 (GH 13965)与
feather-format集成,包括新的顶层pd.read_feather()和DataFrame.to_feather()方法,详见 此处。Series.str.replace()现在接受一个可调用对象作为替换,该对象会传递给re.sub(GH 15055)Series.str.replace()现在接受编译后的正则表达式作为模式 (GH 15446)Series.sort_index接受参数kind和na_position(GH 13589, GH 14444)DataFrame和DataFrame.groupby()增加了nunique()方法,用于计算轴上的不同值 (GH 14336, GH 15197)。DataFrame增加了melt()方法,等同于pd.melt(),用于将宽格式转换为长格式 (GH 12640)。当使用
sheetname=None时,pd.read_excel()现在会保留工作表的顺序 (GH 9930)现在支持带有小数点的多个偏移量别名(例如,
0.5min被解析为30s)(GH 8419)已将
.isnull()和.notnull()添加到Index对象,使其与SeriesAPI 更一致 (GH 15300)当索引/切片到未排序的 MultiIndex 时,会抛出新的
UnsortedIndexError(KeyError的子类)(GH 11897)。这允许区分由于未排序或键错误引起的错误。详见 此处MultiIndex增加了.to_frame()方法,用于转换为DataFrame(GH 12397)pd.cut和pd.qcut现在支持 datetime64 和 timedelta64 dtypes (GH 14714, GH 14798)pd.qcut增加了duplicates='raise'|'drop'选项,用于控制是否在重复边界处抛出错误 (GH 7751)Series提供to_excel方法以输出 Excel 文件 (GH 8825)pd.read_csv()中的usecols参数现在接受可调用函数作为值 (GH 14154)pd.read_csv()中的skiprows参数现在接受可调用函数作为值 (GH 10882)如果
nrows和chunksize参数在pd.read_csv()中同时传入,则支持这两个参数 (GH 6774, GH 15755)DataFrame.plot现在会在每个子图上方打印标题,如果subplots=True且title是字符串列表 (GH 14753)DataFrame.plot可以将 matplotlib 2.0 默认颜色循环作为单个字符串作为颜色参数传递,详见 此处。(GH 15516)Series.interpolate()现在支持以 timedelta 作为索引类型并使用method='time'(GH 6424)DataFrame/Series.rename新增level关键字,用于重命名 MultiIndex 中指定级别的标签 (GH 4160)。DataFrame.reset_index()现在将元组index.name解释为跨越columns级别的键,如果columns是MultiIndex(GH 16164)新增
Timedelta.isoformat方法,用于将 Timedelta 格式化为 ISO 8601 持续时间。详见 Timedelta 文档 (GH 15136).select_dtypes()现在允许使用字符串datetimetz来通用选择带有时区的日期时间 (GH 14910).to_latex()方法现在将接受multicolumn和multirow参数,以使用附带的 LaTeX 增强功能pd.merge_asof()增加了direction='backward'|'forward'|'nearest'选项 (GH 14887)Series/DataFrame.asfreq()增加了fill_value参数,用于填充缺失值 (GH 3715)。Series/DataFrame.resample.asfreq增加了fill_value参数,用于在重采样期间填充缺失值 (GH 3715)。pandas.util.hash_pandas_object()获得了对MultiIndex进行哈希的能力 (GH 15224)Series/DataFrame.squeeze()增加了axis参数。(GH 15339)DataFrame.to_excel()有一个新的freeze_panes参数,用于在导出到 Excel 时打开“冻结窗格”功能 (GH 15160)pd.read_html()将解析多个标题行,创建一个 MultiIndex 标题。(GH 13434)。HTML 表格输出如果
colspan或rowspan属性等于 1 则跳过。(GH 15403)pandas.io.formats.style.Styler模板现在包含块,以便更轻松地扩展,请参阅 示例 Notebook (GH 15649)Styler.render()现在接受**kwargs以允许在模板中使用用户定义的变量 (GH 15649)与 Jupyter notebook 5.0 兼容;MultiIndex 列标签左对齐,MultiIndex 行标签顶对齐 (GH 15379)
TimedeltaIndex现在有一个自定义日期刻度格式器,专门为纳秒级精度设计 (GH 8711)pd.api.types.union_categoricals增加了ignore_ordered参数,以允许忽略合并分类的有序属性 (GH 13410)。有关更多信息,请参阅 分类联合文档。DataFrame.to_latex()和DataFrame.to_string()现在允许可选的标题别名。(GH 15536)重新启用
pd.read_excel()的parse_dates关键字,以将字符串列解析为日期 (GH 14326)向
Index的子类添加了.empty属性。(GH 15270)启用
Timedelta和TimedeltaIndex的地板除法 (GH 15828)pandas.io.json.json_normalize()增加了errors='ignore'|'raise'选项;默认值为errors='raise',这是向后兼容的。(GH 14583)带有空
list的pandas.io.json.json_normalize()将返回一个空的DataFrame(GH 15534)pandas.io.json.json_normalize()增加了一个sep选项,接受str用于分隔连接字段;默认值为“.”,这是向后兼容的。(GH 14883)已添加
MultiIndex.remove_unused_levels()以方便 移除未使用的级别。(GH 15694)pd.read_csv()现在会在发生任何解析错误时抛出ParserError错误 (GH 15913, GH 15925)pd.read_csv()现在支持 Python 解析器的error_bad_lines和warn_bad_lines参数 (GH 15925)display.show_dimensions选项现在也可以用于指定Series的长度是否应在其 repr 中显示 (GH 7117)。parallel_coordinates()增加了一个sort_labels关键字参数,用于对类别标签及其分配的颜色进行排序 (GH 15908)添加了选项,允许打开/关闭使用
bottleneck和numexpr,详见 此处 (GH 16157)DataFrame.style.bar()现在接受另外两个选项来进一步自定义条形图。条形对齐方式设置为align='left'|'mid'|'zero',默认值为“left”,这是向后兼容的;您现在可以传递一个color=[color_negative, color_positive]列表。(GH 14757)
向后不兼容的 API 更改#
使用 pandas < 0.13.0 创建的 HDF5 格式可能存在不兼容性#
pd.TimeSeries 在 0.17.0 版本中已正式弃用,尽管自 0.13.0 版本以来它一直是别名。它已被删除,转而使用 pd.Series。(GH 15098)。
这*可能*会导致早期版本中创建的 HDF5 文件在使用了 pd.TimeSeries 的情况下无法读取。这种情况最有可能发生在 pandas < 0.13.0 版本。如果您遇到此情况,可以使用最近的早期 pandas 版本读取 HDF5 文件,然后在应用以下过程后重新写入。
In [2]: s = pd.TimeSeries([1, 2, 3], index=pd.date_range('20130101', periods=3))
In [3]: s
Out[3]:
2013-01-01 1
2013-01-02 2
2013-01-03 3
Freq: D, dtype: int64
In [4]: type(s)
Out[4]: pandas.core.series.TimeSeries
In [5]: s = pd.Series(s)
In [6]: s
Out[6]:
2013-01-01 1
2013-01-02 2
2013-01-03 3
Freq: D, dtype: int64
In [7]: type(s)
Out[7]: pandas.core.series.Series
Index 类型上的 Map 现在返回其他 Index 类型#
Index 上的 map 现在返回 Index,而不是 numpy 数组 (GH 12766)
In [56]: idx = pd.Index([1, 2])
In [57]: idx
Out[57]: Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
In [58]: mi = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([(1, 2), (2, 4)])
In [59]: mi
Out[59]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
之前的行为
In [5]: idx.map(lambda x: x * 2)
Out[5]: array([2, 4])
In [6]: idx.map(lambda x: (x, x * 2))
Out[6]: array([(1, 2), (2, 4)], dtype=object)
In [7]: mi.map(lambda x: x)
Out[7]: array([(1, 2), (2, 4)], dtype=object)
In [8]: mi.map(lambda x: x[0])
Out[8]: array([1, 2])
新行为
In [60]: idx.map(lambda x: x * 2)
Out[60]: Index([2, 4], dtype='int64')
In [61]: idx.map(lambda x: (x, x * 2))
Out[61]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
In [62]: mi.map(lambda x: x)
Out[62]:
MultiIndex([(1, 2),
(2, 4)],
)
In [63]: mi.map(lambda x: x[0])
Out[63]: Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
Series 上具有 datetime64 值时,map 可能会返回 int64 dtypes 而不是 int32
In [64]: s = pd.Series(pd.date_range('2011-01-02T00:00', '2011-01-02T02:00', freq='H')
....: .tz_localize('Asia/Tokyo'))
....:
In [65]: s
Out[65]:
0 2011-01-02 00:00:00+09:00
1 2011-01-02 01:00:00+09:00
2 2011-01-02 02:00:00+09:00
Length: 3, dtype: datetime64[ns, Asia/Tokyo]
之前的行为
In [9]: s.map(lambda x: x.hour)
Out[9]:
0 0
1 1
2 2
dtype: int32
新行为
In [66]: s.map(lambda x: x.hour)
Out[66]:
0 0
1 1
2 2
Length: 3, dtype: int64
访问 Index 的 datetime 字段现在返回 Index#
DatetimeIndex、PeriodIndex 和 TimedeltaIndex 的日期时间相关属性(概述见 此处)以前返回 numpy 数组。它们现在将返回一个新的 Index 对象,除了布尔字段的情况,结果仍将是布尔 ndarray。(GH 15022)
之前的行为
In [1]: idx = pd.date_range("2015-01-01", periods=5, freq='10H')
In [2]: idx.hour
Out[2]: array([ 0, 10, 20, 6, 16], dtype=int32)
新行为
In [67]: idx = pd.date_range("2015-01-01", periods=5, freq='10H')
In [68]: idx.hour
Out[68]: Index([0, 10, 20, 6, 16], dtype='int32')
这样做的好处是,特定的 Index 方法在结果上仍然可用。另一方面,这可能会导致向后不兼容:例如,与 numpy 数组相比,Index 对象是不可变的。要获取原始 ndarray,您始终可以使用 np.asarray(idx.hour) 进行显式转换。
pd.unique 现在将与扩展类型保持一致#
在之前的版本中,在 Categorical 和带时区感知的数据类型上使用 Series.unique() 和 pandas.unique() 会产生不同的返回类型。现在这些都已保持一致。(GH 15903)
带时区的日期时间
之前的行为
# Series In [5]: pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() Out[5]: array([Timestamp('2016-01-01 00:00:00-0500', tz='US/Eastern')], dtype=object) In [6]: pd.unique(pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) Out[6]: array(['2016-01-01T05:00:00.000000000'], dtype='datetime64[ns]') # Index In [7]: pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() Out[7]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]', freq=None) In [8]: pd.unique([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ...: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]) Out[8]: array(['2016-01-01T05:00:00.000000000'], dtype='datetime64[ns]')
新行为
# Series, returns an array of Timestamp tz-aware In [64]: pd.Series([pd.Timestamp(r'20160101', tz=r'US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp(r'20160101', tz=r'US/Eastern')]).unique() ....: Out[64]: <DatetimeArray> ['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'] Length: 1, dtype: datetime64[ns, US/Eastern] In [65]: pd.unique(pd.Series([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) ....: Out[65]: <DatetimeArray> ['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'] Length: 1, dtype: datetime64[ns, US/Eastern] # Index, returns a DatetimeIndex In [66]: pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')]).unique() ....: Out[66]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]', freq=None) In [67]: pd.unique(pd.Index([pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern'), ....: pd.Timestamp('20160101', tz='US/Eastern')])) ....: Out[67]: DatetimeIndex(['2016-01-01 00:00:00-05:00'], dtype='datetime64[ns, US/Eastern]', freq=None)
分类
之前的行为
In [1]: pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category').unique() Out[1]: [b, a, c] Categories (3, object): [b, a, c] In [2]: pd.unique(pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category')) Out[2]: array(['b', 'a', 'c'], dtype=object)
新行为
# returns a Categorical In [68]: pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category').unique() Out[68]: ['b', 'a', 'c'] Categories (3, object): ['a', 'b', 'c'] In [69]: pd.unique(pd.Series(list('baabc'), dtype='category')) Out[69]: ['b', 'a', 'c'] Categories (3, object): ['a', 'b', 'c']
S3 文件处理#
pandas 现在使用 s3fs 来处理 S3 连接。这应该不会破坏任何代码。然而,由于 s3fs 不是必需的依赖项,您需要单独安装它,就像以前版本的 pandas 中的 boto 一样。(GH 11915)。
部分字符串索引更改#
DatetimeIndex 部分字符串索引 现在作为精确匹配工作,前提是字符串分辨率与索引分辨率一致,包括两者都为秒的情况 (GH 14826)。有关详细信息,请参阅 切片与精确匹配。
In [70]: df = pd.DataFrame({'a': [1, 2, 3]}, pd.DatetimeIndex(['2011-12-31 23:59:59',
....: '2012-01-01 00:00:00',
....: '2012-01-01 00:00:01']))
....:
之前的行为
In [4]: df['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[4]:
a
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
In [5]: df['a']['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[5]:
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
Name: a, dtype: int64
新行为
In [4]: df['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
KeyError: '2011-12-31 23:59:59'
In [5]: df['a']['2011-12-31 23:59:59']
Out[5]: 1
不同浮点 dtype 的 concat 将不会自动向上转换#
以前,concat 多个具有不同 float dtype 的对象会自动将结果向上转换为 float64 dtype。现在将使用最小的可接受 dtype (GH 13247)。
In [71]: df1 = pd.DataFrame(np.array([1.0], dtype=np.float32, ndmin=2))
In [72]: df1.dtypes
Out[72]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
In [73]: df2 = pd.DataFrame(np.array([np.nan], dtype=np.float32, ndmin=2))
In [74]: df2.dtypes
Out[74]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
之前的行为
In [7]: pd.concat([df1, df2]).dtypes
Out[7]:
0 float64
dtype: object
新行为
In [75]: pd.concat([df1, df2]).dtypes
Out[75]:
0 float32
Length: 1, dtype: object
pandas Google BigQuery 支持已迁移#
pandas 已将 Google BigQuery 支持分拆到单独的软件包 pandas-gbq 中。您可以通过 conda install pandas-gbq -c conda-forge 或 pip install pandas-gbq 来获取它。read_gbq() 和 DataFrame.to_gbq() 的功能在当前发布的 pandas-gbq=0.1.4 版本中保持不变。文档现已托管在 此处 (GH 15347)。
Index 的内存使用更准确#
在以前的版本中,在带有索引的 pandas 结构上显示 .memory_usage() 只会包含实际的索引值,而不包括用于快速索引的结构。这对于 Index 和 MultiIndex 通常会有所不同,而对于其他索引类型则差异较小。(GH 15237)
之前的行为
In [8]: index = pd.Index(['foo', 'bar', 'baz'])
In [9]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[9]: 180
In [10]: index.get_loc('foo')
Out[10]: 0
In [11]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[11]: 180
新行为
In [8]: index = pd.Index(['foo', 'bar', 'baz'])
In [9]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[9]: 180
In [10]: index.get_loc('foo')
Out[10]: 0
In [11]: index.memory_usage(deep=True)
Out[11]: 260
DataFrame.sort_index 更改#
在某些情况下,在 MultiIndexed DataFrame 上调用 .sort_index() 会返回*相同的* DataFrame,而似乎没有排序。这会在 lexsorted 但非单调级别的情况下发生。(GH 15622, GH 15687, GH 14015, GH 13431, GH 15797)
这与以前的版本*未改变*,但为了说明目的而显示
In [81]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.arange(6), columns=['value'],
....: index=pd.MultiIndex.from_product([list('BA'), range(3)]))
....:
In [82]: df
Out[82]:
value
B 0 0
1 1
2 2
A 0 3
1 4
2 5
[6 rows x 1 columns]
In [87]: df.index.is_lexsorted()
Out[87]: False
In [88]: df.index.is_monotonic
Out[88]: False
排序按预期工作
In [76]: df.sort_index()
Out[76]:
a
2011-12-31 23:59:59 1
2012-01-01 00:00:00 2
2012-01-01 00:00:01 3
[3 rows x 1 columns]
In [90]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[90]: True
In [91]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[91]: True
然而,这个例子,它的第二个级别不是单调的,行为不如预期。
In [77]: df = pd.DataFrame({'value': [1, 2, 3, 4]},
....: index=pd.MultiIndex([['a', 'b'], ['bb', 'aa']],
....: [[0, 0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0, 1]]))
....:
In [78]: df
Out[78]:
value
a bb 1
aa 2
b bb 3
aa 4
[4 rows x 1 columns]
之前的行为
In [11]: df.sort_index()
Out[11]:
value
a bb 1
aa 2
b bb 3
aa 4
In [14]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[14]: True
In [15]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[15]: False
新行为
In [94]: df.sort_index()
Out[94]:
value
a aa 2
bb 1
b aa 4
bb 3
[4 rows x 1 columns]
In [95]: df.sort_index().index.is_lexsorted()
Out[95]: True
In [96]: df.sort_index().index.is_monotonic
Out[96]: True
GroupBy describe 格式#
groupby.describe() 的输出格式现在在列中而不是索引中标记 describe() 指标。这种格式与 groupby.agg() 在一次应用多个函数时保持一致。(GH 4792)
之前的行为
In [1]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 2, 2], 'B': [1, 2, 3, 4]})
In [2]: df.groupby('A').describe()
Out[2]:
B
A
1 count 2.000000
mean 1.500000
std 0.707107
min 1.000000
25% 1.250000
50% 1.500000
75% 1.750000
max 2.000000
2 count 2.000000
mean 3.500000
std 0.707107
min 3.000000
25% 3.250000
50% 3.500000
75% 3.750000
max 4.000000
In [3]: df.groupby('A').agg(["mean", "std", "min", "max"])
Out[3]:
B
mean std amin amax
A
1 1.5 0.707107 1 2
2 3.5 0.707107 3 4
新行为
In [79]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 2, 2], 'B': [1, 2, 3, 4]})
In [80]: df.groupby('A').describe()
Out[80]:
B
count mean std min 25% 50% 75% max
A
1 2.0 1.5 0.707107 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.75 2.0
2 2.0 3.5 0.707107 3.0 3.25 3.5 3.75 4.0
[2 rows x 8 columns]
In [81]: df.groupby('A').agg(["mean", "std", "min", "max"])
Out[81]:
B
mean std min max
A
1 1.5 0.707107 1 2
2 3.5 0.707107 3 4
[2 rows x 4 columns]
窗口二元 corr/cov 操作返回 MultiIndex DataFrame#
当对 .rolling(..)、.expanding(..) 或 .ewm(..) 对象进行二元窗口操作(如 .corr() 或 .cov())时,现在将返回一个 2 级 MultiIndexed DataFrame,而不是 Panel,因为 Panel 现已弃用,详见 此处。它们在功能上等效,但 MultiIndexed DataFrame 在 pandas 中获得更多支持。有关更多信息,请参阅 窗口二元操作 部分。(GH 15677)
In [82]: np.random.seed(1234)
In [83]: df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.rand(100, 2),
....: columns=pd.Index(['A', 'B'], name='bar'),
....: index=pd.date_range('20160101',
....: periods=100, freq='D', name='foo'))
....:
In [84]: df.tail()
Out[84]:
bar A B
foo
2016-04-05 0.640880 0.126205
2016-04-06 0.171465 0.737086
2016-04-07 0.127029 0.369650
2016-04-08 0.604334 0.103104
2016-04-09 0.802374 0.945553
[5 rows x 2 columns]
之前的行为
In [2]: df.rolling(12).corr()
Out[2]:
<class 'pandas.core.panel.Panel'>
Dimensions: 100 (items) x 2 (major_axis) x 2 (minor_axis)
Items axis: 2016-01-01 00:00:00 to 2016-04-09 00:00:00
Major_axis axis: A to B
Minor_axis axis: A to B
新行为
In [85]: res = df.rolling(12).corr()
In [86]: res.tail()
Out[86]:
bar A B
foo bar
2016-04-07 B -0.132090 1.000000
2016-04-08 A 1.000000 -0.145775
B -0.145775 1.000000
2016-04-09 A 1.000000 0.119645
B 0.119645 1.000000
[5 rows x 2 columns]
检索横截面的相关矩阵
In [87]: df.rolling(12).corr().loc['2016-04-07']
Out[87]:
bar A B
bar
A 1.00000 -0.13209
B -0.13209 1.00000
[2 rows x 2 columns]
HDFStore 字符串比较#
在以前的版本中,大多数类型可以与 HDFStore 中的字符串列进行比较,通常会导致无效比较,返回一个空结果帧。这些比较现在将引发 TypeError (GH 15492)
In [88]: df = pd.DataFrame({'unparsed_date': ['2014-01-01', '2014-01-01']})
In [89]: df.to_hdf('store.h5', key='key', format='table', data_columns=True)
In [90]: df.dtypes
Out[90]:
unparsed_date object
Length: 1, dtype: object
之前的行为
In [4]: pd.read_hdf('store.h5', 'key', where='unparsed_date > ts')
File "<string>", line 1
(unparsed_date > 1970-01-01 00:00:01.388552400)
^
SyntaxError: invalid token
新行为
In [18]: ts = pd.Timestamp('2014-01-01')
In [19]: pd.read_hdf('store.h5', 'key', where='unparsed_date > ts')
TypeError: Cannot compare 2014-01-01 00:00:00 of
type <class 'pandas.tslib.Timestamp'> to string column
Index.intersection 和内连接现在保留左 Index 的顺序#
Index.intersection() 现在保留调用 Index(左侧)的顺序,而不是另一个 Index(右侧)的顺序 (GH 15582)。这会影响内连接、DataFrame.join() 和 merge(),以及 .align 方法。
Index.intersectionIn [91]: left = pd.Index([2, 1, 0]) In [92]: left Out[92]: Index([2, 1, 0], dtype='int64') In [93]: right = pd.Index([1, 2, 3]) In [94]: right Out[94]: Index([1, 2, 3], dtype='int64')
之前的行为
In [4]: left.intersection(right) Out[4]: Int64Index([1, 2], dtype='int64')
新行为
In [95]: left.intersection(right) Out[95]: Index([2, 1], dtype='int64')
DataFrame.join和pd.mergeIn [96]: left = pd.DataFrame({'a': [20, 10, 0]}, index=[2, 1, 0]) In [97]: left Out[97]: a 2 20 1 10 0 0 [3 rows x 1 columns] In [98]: right = pd.DataFrame({'b': [100, 200, 300]}, index=[1, 2, 3]) In [99]: right Out[99]: b 1 100 2 200 3 300 [3 rows x 1 columns]
之前的行为
In [4]: left.join(right, how='inner') Out[4]: a b 1 10 100 2 20 200
新行为
In [100]: left.join(right, how='inner') Out[100]: a b 2 20 200 1 10 100 [2 rows x 2 columns]
Pivot 表格总是返回 DataFrame#
pivot_table() 的文档声明它*总是*返回一个 DataFrame。这里修复了一个错误,该错误允许它在某些情况下返回一个 Series。(GH 4386)
In [101]: df = pd.DataFrame({'col1': [3, 4, 5],
.....: 'col2': ['C', 'D', 'E'],
.....: 'col3': [1, 3, 9]})
.....:
In [102]: df
Out[102]:
col1 col2 col3
0 3 C 1
1 4 D 3
2 5 E 9
[3 rows x 3 columns]
之前的行为
In [2]: df.pivot_table('col1', index=['col3', 'col2'], aggfunc="sum")
Out[2]:
col3 col2
1 C 3
3 D 4
9 E 5
Name: col1, dtype: int64
新行为
In [103]: df.pivot_table('col1', index=['col3', 'col2'], aggfunc="sum")
Out[103]:
col1
col3 col2
1 C 3
3 D 4
9 E 5
[3 rows x 1 columns]
其他 API 更改#
numexpr版本现在要求 >= 2.4.6,如果不满足此要求,将完全不使用它 (GH 15213)。CParserError在pd.read_csv()中已重命名为ParserError,并将在未来移除 (GH 12665)SparseArray.cumsum()和SparseSeries.cumsum()现在将分别始终返回SparseArray和SparseSeries(GH 12855)带有空
DataFrame的DataFrame.applymap()将返回空DataFrame的副本,而不是Series(GH 8222)Series.map()现在尊重具有__missing__方法的字典子类的默认值,例如collections.Counter(GH 15999).loc与.ix兼容,可以接受迭代器和具名元组 (GH 15120)interpolate()和fillna()如果limit关键字参数不大于 0,将引发ValueError。(GH 9217)pd.read_csv()现在将在dialect参数和用户提供的值发生冲突时发出ParserWarning(GH 14898)pd.read_csv()对于 C 引擎,如果引号字符大于一个字节,现在将引发ValueError(GH 11592)inplace参数现在需要一个布尔值,否则会抛出ValueError(GH 14189)pandas.api.types.is_datetime64_ns_dtype现在将对时区感知 dtype 报告True,类似于pandas.api.types.is_datetime64_any_dtypeDataFrame.asof()如果未找到匹配项,将返回一个填充了空值的Series,而不是标量NaN(GH 15118)对 NDFrame 对象的
copy.copy()和copy.deepcopy()函数的特定支持 (GH 15444)Series.sort_values()接受一个包含一个布尔值的列表,以与DataFrame.sort_values()的行为保持一致 (GH 15604).merge()和.join()在categorydtype 列上操作时,现在会尽可能保留 category dtype (GH 10409)SparseDataFrame.default_fill_value将为 0,以前从pd.get_dummies(..., sparse=True)返回时为nan(GH 15594)Series.str.match的默认行为已从提取组更改为匹配模式。提取行为自 pandas 0.13.0 版本以来已弃用,可以通过Series.str.extract方法完成 (GH 5224)。因此,as_indexer关键字被忽略(不再需要指定新行为)并被弃用。NaT现在将正确地报告日期时间布尔操作(如is_month_start)的False(GH 15781)NaT现在将为Timedelta和Period访问器(如days和quarter)正确返回np.nan(GH 15782)NaT现在将为tz_localize和tz_convert方法返回NaT(GH 15830)DataFrame和Panel构造函数在输入无效且未指定轴时,现在将引发ValueError而不是PandasError(GH 15541)DataFrame和Panel构造函数在输入无效且未指定轴时,现在将引发ValueError而不是pandas.core.common.PandasError;异常PandasError也被移除。(GH 15541)异常
pandas.core.common.AmbiguousIndexError已被移除,因为它未被引用 (GH 15541)
库的重组:隐私更改#
模块隐私已更改#
一些以前的公共 python/c/c++/cython 扩展模块已被移动和/或重命名。这些都已从公共 API 中移除。此外,pandas.core、pandas.compat 和 pandas.util 顶级模块现在被视为私有。如果指示,引用这些模块将发出弃用警告。(GH 12588)
旧位置 |
新位置 |
已弃用 |
|---|---|---|
pandas.lib |
pandas._libs.lib |
X |
pandas.tslib |
pandas._libs.tslib |
X |
pandas.computation |
pandas.core.computation |
X |
pandas.msgpack |
pandas.io.msgpack |
|
pandas.index |
pandas._libs.index |
|
pandas.algos |
pandas._libs.algos |
|
pandas.hashtable |
pandas._libs.hashtable |
|
pandas.indexes |
pandas.core.indexes |
|
pandas.json |
pandas._libs.json / pandas.io.json |
X |
pandas.parser |
pandas._libs.parsers |
X |
pandas.formats |
pandas.io.formats |
|
pandas.sparse |
pandas.core.sparse |
|
pandas.tools |
pandas.core.reshape |
X |
pandas.types |
pandas.core.dtypes |
X |
pandas.io.sas.saslib |
pandas.io.sas._sas |
|
pandas._join |
pandas._libs.join |
|
pandas._hash |
pandas._libs.hashing |
|
pandas._period |
pandas._libs.period |
|
pandas._sparse |
pandas._libs.sparse |
|
pandas._testing |
pandas._libs.testing |
|
pandas._window |
pandas._libs.window |
创建了一些新的子包,它们具有未直接在顶级命名空间中公开的公共功能:pandas.errors、pandas.plotting 和 pandas.testing(更多详细信息见下文)。连同 pandas.api.types 以及 pandas.io 和 pandas.tseries 子模块中的某些函数,这些现在是公共子包。
进一步更改
函数
union_categoricals()现在可以从pandas.api.types导入,以前是从pandas.types.concat导入 (GH 15998)类型导入
pandas.tslib.NaTType已弃用,可以使用type(pandas.NaT)代替 (GH 16146)pandas.tools.hashing中的公共函数已从该位置弃用,但现在可以从pandas.util导入 (GH 16223)pandas.util中的模块:decorators、print_versions、doctools、validators、depr_module现已设为私有。只有在pandas.util本身中公开的函数才是公共的 (GH 16223)
pandas.errors#
我们正在为所有 pandas 异常和警告添加一个标准的公共模块 pandas.errors。 (GH 14800)。以前,这些异常和警告可以从 pandas.core.common 或 pandas.io.common 导入。这些异常和警告将在未来的版本中从 *.common 位置移除。 (GH 15541)
以下现在是此 API 的一部分
['DtypeWarning',
'EmptyDataError',
'OutOfBoundsDatetime',
'ParserError',
'ParserWarning',
'PerformanceWarning',
'UnsortedIndexError',
'UnsupportedFunctionCall']
pandas.testing#
我们正在添加一个标准模块,用于公开 pandas.testing 中的公共测试函数 (GH 9895)。这些函数可以在为使用 pandas 对象的函数编写测试时使用。
以下测试函数现在是此 API 的一部分
pandas.plotting#
已添加一个新的公共 pandas.plotting 模块,其中包含以前位于 pandas.tools.plotting 或顶层命名空间中的绘图功能。有关更多详细信息,请参阅弃用部分。
其他开发变更#
弃用#
弃用 .ix#
.ix 索引器已弃用,取而代之的是更严格的 .iloc 和 .loc 索引器。.ix 在推断用户想要做什么方面提供了很多“魔法”。更具体地说,.ix 可以根据索引的数据类型决定是按位置索引还是通过标签索引。多年来,这导致了相当多的用户困惑。完整的索引文档请参阅此处。 (GH 14218)
推荐的索引方法是
.loc如果您想进行标签索引.iloc如果您想进行位置索引。
现在使用 .ix 将显示一个 DeprecationWarning,并附有如何转换代码的一些示例的链接此处。
In [104]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3],
.....: 'B': [4, 5, 6]},
.....: index=list('abc'))
.....:
In [105]: df
Out[105]:
A B
a 1 4
b 2 5
c 3 6
[3 rows x 2 columns]
以前的行为,如果您希望从索引的“A”列中获取第0个和第2个元素。
In [3]: df.ix[[0, 2], 'A']
Out[3]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, dtype: int64
使用 .loc。这里我们将从索引中选择适当的索引,然后使用标签索引。
In [106]: df.loc[df.index[[0, 2]], 'A']
Out[106]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, Length: 2, dtype: int64
使用 .iloc。这里我们将获取“A”列的位置,然后使用位置索引来选择内容。
In [107]: df.iloc[[0, 2], df.columns.get_loc('A')]
Out[107]:
a 1
c 3
Name: A, Length: 2, dtype: int64
弃用 Panel#
Panel 已弃用,并将在未来版本中移除。表示 3 维数据的推荐方式是通过 to_frame() 方法在 DataFrame 上使用 MultiIndex,或者使用 xarray 包。pandas 提供了 to_xarray() 方法来自动化此转换 (GH 13563)。
In [133]: import pandas._testing as tm
In [134]: p = tm.makePanel()
In [135]: p
Out[135]:
<class 'pandas.core.panel.Panel'>
Dimensions: 3 (items) x 3 (major_axis) x 4 (minor_axis)
Items axis: ItemA to ItemC
Major_axis axis: 2000-01-03 00:00:00 to 2000-01-05 00:00:00
Minor_axis axis: A to D
转换为 MultiIndex DataFrame
In [136]: p.to_frame()
Out[136]:
ItemA ItemB ItemC
major minor
2000-01-03 A 0.628776 -1.409432 0.209395
B 0.988138 -1.347533 -0.896581
C -0.938153 1.272395 -0.161137
D -0.223019 -0.591863 -1.051539
2000-01-04 A 0.186494 1.422986 -0.592886
B -0.072608 0.363565 1.104352
C -1.239072 -1.449567 0.889157
D 2.123692 -0.414505 -0.319561
2000-01-05 A 0.952478 -2.147855 -1.473116
B -0.550603 -0.014752 -0.431550
C 0.139683 -1.195524 0.288377
D 0.122273 -1.425795 -0.619993
[12 rows x 3 columns]
转换为 xarray DataArray
In [137]: p.to_xarray()
Out[137]:
<xarray.DataArray (items: 3, major_axis: 3, minor_axis: 4)>
array([[[ 0.628776, 0.988138, -0.938153, -0.223019],
[ 0.186494, -0.072608, -1.239072, 2.123692],
[ 0.952478, -0.550603, 0.139683, 0.122273]],
[[-1.409432, -1.347533, 1.272395, -0.591863],
[ 1.422986, 0.363565, -1.449567, -0.414505],
[-2.147855, -0.014752, -1.195524, -1.425795]],
[[ 0.209395, -0.896581, -0.161137, -1.051539],
[-0.592886, 1.104352, 0.889157, -0.319561],
[-1.473116, -0.43155 , 0.288377, -0.619993]]])
Coordinates:
* items (items) object 'ItemA' 'ItemB' 'ItemC'
* major_axis (major_axis) datetime64[ns] 2000-01-03 2000-01-04 2000-01-05
* minor_axis (minor_axis) object 'A' 'B' 'C' 'D'
弃用 groupby.agg() 在重命名时使用字典#
.groupby(..).agg(..)、.rolling(..).agg(..) 和 .resample(..).agg(..) 语法可以接受多种输入,包括标量、列表以及将列名映射到标量或列表的字典。这提供了一种有用的语法,用于构建多个(可能不同)聚合。
然而,.agg(..) 也可以接受一个允许对结果列进行“重命名”的字典。这是一种复杂且令人困惑的语法,并且在 Series 和 DataFrame 之间不一致。我们正在弃用此“重命名”功能。
我们正在弃用向分组/滚动/重采样的
Series传递字典。这允许用户rename结果聚合,但这与向分组的DataFrame传递字典具有完全不同的含义,后者接受列到聚合的映射。我们以类似的方式弃用向分组/滚动/重采样的
DataFrame传递字典的字典。
这是一个说明性示例
In [108]: df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 1, 1, 2, 2],
.....: 'B': range(5),
.....: 'C': range(5)})
.....:
In [109]: df
Out[109]:
A B C
0 1 0 0
1 1 1 1
2 1 2 2
3 2 3 3
4 2 4 4
[5 rows x 3 columns]
这是一个计算不同列的不同聚合的典型有用语法。这是一种自然且有用的语法。我们通过获取指定列并应用函数列表来从字典到列表进行聚合。这会为列返回一个 MultiIndex(这未弃用)。
In [110]: df.groupby('A').agg({'B': 'sum', 'C': 'min'})
Out[110]:
B C
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
[2 rows x 2 columns]
这是第一个弃用示例,将字典传递给分组的 Series。这是聚合和重命名的组合
In [6]: df.groupby('A').B.agg({'foo': 'count'})
FutureWarning: using a dict on a Series for aggregation
is deprecated and will be removed in a future version
Out[6]:
foo
A
1 3
2 2
您可以更地道地完成相同的操作,方法是
In [111]: df.groupby('A').B.agg(['count']).rename(columns={'count': 'foo'})
Out[111]:
foo
A
1 3
2 2
[2 rows x 1 columns]
这是第二个弃用示例,将字典的字典传递给分组的 DataFrame
In [23]: (df.groupby('A')
...: .agg({'B': {'foo': 'sum'}, 'C': {'bar': 'min'}})
...: )
FutureWarning: using a dict with renaming is deprecated and
will be removed in a future version
Out[23]:
B C
foo bar
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
您可以通过以下方式实现几乎相同的效果
In [112]: (df.groupby('A')
.....: .agg({'B': 'sum', 'C': 'min'})
.....: .rename(columns={'B': 'foo', 'C': 'bar'})
.....: )
.....:
Out[112]:
foo bar
A
1 3 0
2 7 3
[2 rows x 2 columns]
弃用 .plotting#
pandas.tools.plotting 模块已弃用,取而代之的是顶层 pandas.plotting 模块。所有公共绘图函数现在都可以从 pandas.plotting 获得 (GH 12548)。
此外,顶层 pandas.scatter_matrix 和 pandas.plot_params 已弃用。用户也可以从 pandas.plotting 导入这些。
以前的脚本
pd.tools.plotting.scatter_matrix(df)
pd.scatter_matrix(df)
应改为
pd.plotting.scatter_matrix(df)
其他弃用#
SparseArray.to_dense()已弃用fill参数,因为该参数未被遵守 (GH 14647)SparseSeries.to_dense()已弃用sparse_only参数 (GH 14647)Series.repeat()已弃用reps参数,转而使用repeats(GH 12662)Series构造函数和.astype方法已弃用接受没有频率的时间戳 dtypes(例如np.datetime64)作为dtype参数 (GH 15524)Index.repeat()和MultiIndex.repeat()已弃用n参数,转而使用repeats(GH 12662)Categorical.searchsorted()和Series.searchsorted()已弃用v参数,转而使用value(GH 12662)TimedeltaIndex.searchsorted()、DatetimeIndex.searchsorted()和PeriodIndex.searchsorted()已弃用key参数,转而使用value(GH 12662)DataFrame.astype()已弃用raise_on_error参数,转而使用errors(GH 14878)Series.sortlevel和DataFrame.sortlevel已弃用,转而使用Series.sort_index和DataFrame.sort_index(GH 15099)从
pandas.tools.merge导入concat已弃用,转而支持从pandas命名空间导入。这只应影响显式导入 (GH 15358)Series/DataFrame/Panel.consolidate()已作为公共方法弃用。 (GH 15483)Series.str.match()的as_indexer关键字已弃用(被忽略的关键字) (GH 15257)。以下顶层 pandas 函数已弃用,并将在未来版本中移除 (GH 13790, GH 15940)
pd.pnow(),已被Period.now()替换pd.Term已移除,因为它不适用于用户代码。在 HDFStore 中搜索时,请改用 where 子句中的内联字符串表达式pd.Expr已移除,因为它不适用于用户代码。pd.match()已移除。pd.groupby(),已被直接在Series/DataFrame上使用.groupby()方法替换pd.get_store(),已被直接调用pd.HDFStore(...)替换
is_any_int_dtype、is_floating_dtype和is_sequence已从pandas.api.types弃用 (GH 16042)
移除先前版本的弃用/更改#
带有
google-analytics接口的pandas.io.ga模块已移除 (GH 11308)。类似功能可在 Google2Pandas 包中找到。pd.to_datetime和pd.to_timedelta已弃用coerce参数,转而使用errors(GH 13602)pandas.stats.fama_macbeth、pandas.stats.ols、pandas.stats.plm和pandas.stats.var,以及顶层例程pandas.fama_macbeth和pandas.ols已移除。类似功能可在 statsmodels 包中找到。(GH 11898)TimeSeries和SparseTimeSeries类,即Series和SparseSeries的别名,已移除 (GH 10890, GH 15098)。Series.is_time_series已弃用,转而使用Series.index.is_all_dates(GH 15098)已弃用的
irow、icol、iget和iget_value方法已移除,转而使用iloc和iat,如 此处 所述 (GH 10711)。已弃用的
DataFrame.iterkv()已移除,转而使用DataFrame.iteritems()(GH 10711)Categorical构造函数已弃用name参数 (GH 10632)Categorical已放弃对NaN类别dtypes的支持 (GH 10748)take_last参数已从duplicated()、drop_duplicates()、nlargest()和nsmallest()方法中移除 (GH 10236, GH 10792, GH 10920)Series、Index和DataFrame已移除sort和order方法 (GH 10726)pytables中的 where 子句仅接受字符串和表达式类型,而不接受其他数据类型 (GH 12027)DataFrame已移除combineAdd和combineMult方法,转而分别使用add和mul(GH 10735)
性能改进#
改进了
pd.wide_to_long()的性能 (GH 14779)通过在
objectdtype 被推断为字符串时释放 GIL,改进了pd.factorize()的性能 (GH 14859, GH 16057)改进了使用不规则 DatetimeIndex(或
compat_x=True)进行时间序列绘图的性能 (GH 15073)。改进了
groupby().cummin()和groupby().cummax()的性能 (GH 15048, GH 15109, GH 15561, GH 15635)使用
MultiIndex索引时,性能得到改进,内存使用减少 (GH 15245)在
read_sas()方法中读取缓冲区对象时,如果未指定格式,则推断文件路径字符串而不是缓冲区对象。(GH 14947)改进了分类数据的
.rank()性能 (GH 15498)改进了使用
.unstack()时的性能 (GH 15503)改进了
category列的合并/连接性能 (GH 10409)改进了
bool列的drop_duplicates()性能 (GH 12963)改进了
pd.core.groupby.GroupBy.apply在应用函数使用 group DataFrame 的.name属性时的性能 (GH 15062)。改进了使用列表或数组进行
iloc索引的性能 (GH 15504)。改进了具有单调索引的
Series.sort_index()性能 (GH 15694)在某些平台使用缓冲读取时,
pd.read_csv()的性能得到改进 (GH 16039)
Bug 修复#
转换#
Timestamp.replace中的一个 bug,现在在给定不正确的参数名称时会引发TypeError;以前会引发ValueError(GH 15240)Timestamp.replace中与传递长整型的兼容性 bug (GH 15030)TimedeltaIndex加法中允许溢出而不报错的 bug (GH 14816)TimedeltaIndex在使用loc进行布尔索引时引发ValueError的 bug (GH 14946)捕获
Timestamp+Timedelta/Offset操作中溢出的 bug (GH 15126)DatetimeIndex.round()和Timestamp.round()在以毫秒或更小单位进行舍入时浮点精度问题的 bug (GH 14440, GH 15578)astype()中inf值被错误转换为整数的 bug。现在,对 Series 和 DataFrames 使用astype()时会引发错误 (GH 14265)DataFrame(..).apply(to_numeric)在值类型为 decimal.Decimal 时的 bug。(GH 14827)describe()中,当传递一个不包含中位数的 numpy 数组到percentiles关键字参数时的 bug (GH 14908)清理了
PeriodIndex构造函数,包括更一致地对浮点数引发错误 (GH 13277)在空 NDFrame 对象上使用
__deepcopy__的 bug (GH 15370)Series.replace和DataFrame.replace在遇到空替换字典时失败的 bug (GH 15289)Series.replace将数字替换为字符串的 bug (GH 15743)Index构造中,当存在NaN元素并指定整数 dtype 时的 bug (GH 15187)Series构造中,当存在时区感知日期时间时的 bug (GH 14928)Series.dt.round()在不同参数下对NaT行为不一致的 bug (GH 14940)Series构造函数中,当同时提供copy=True和dtype参数时的 bug (GH 15125)空
DataFrame与常量进行比较方法(例如,lt、gt等)返回的Seriesdtype 不正确的 bug (GH 15077)Series.ffill()中包含时区感知日期时间的混合 dtype 时的 bug。(GH 14956)DataFrame.fillna()中,当 fillna 值为dict类型时,downcast参数被忽略的 bug (GH 15277).asfreq()中,当Series为空时,频率未设置的 bug (GH 14320)DataFrame构造中,当列表式数据包含 nulls 和日期时间时的 bug (GH 15869)DataFrame.fillna()中包含时区感知日期时间的 bug (GH 15855)is_string_dtype、is_timedelta64_ns_dtype和is_string_like_dtype中,当传入None时引发错误的 bug (GH 15941)pd.unique在Categorical上返回类型不正确的 bug,它返回的是 ndarray 而不是Categorical(GH 15903)Index.to_series()中索引未被复制(导致后续修改会改变原始索引)的 bug (GH 15949)在长度为 1 的 DataFrame 中进行部分字符串索引的 bug (GH 16071)
Series构造中,传入无效 dtype 未引发错误的 bug。(GH 15520)
索引#
Index逆运算中的 bug (GH 14973)DataFrame.sort_values()中,当按多列排序且其中一列类型为int64且包含NaT时的 bug (GH 14922)DataFrame.reindex()中,当传入columns时method被忽略的 bug (GH 14992)DataFrame.loc中,使用Series索引器索引MultiIndex时的 bug (GH 14730, GH 15424)DataFrame.loc中,使用 numpy 数组索引MultiIndex时的 bug (GH 15434)Series.asof中,如果 Series 包含所有np.nan则引发错误的 bug (GH 15713).at中,从时区感知列中选择时的 bug (GH 15822)Series.where()和DataFrame.where()中,数组式条件被拒绝的 bug (GH 15414)Series.where()中,时区感知数据被转换为浮点表示的 bug (GH 15701).loc中,对于 DataFrame 的标量访问未返回正确 dtype 的 bug (GH 11617)Categorical.searchsorted()中,使用了字母顺序而不是提供的分类顺序的 bug (GH 14522)Series.iloc中,当列表式索引输入为Categorical对象时,返回的是Categorical对象,而预期是Series的 bug。(GH 14580)DataFrame.isin比较日期时间类型与空帧的 bug (GH 15473).reset_index()中,当MultiIndex中包含全NaN级别时失败的 bug (GH 6322).reset_index()中,当MultiIndex列中已存在索引名称时,引发错误的 bug (GH 16120)使用元组创建
MultiIndex且未传递名称列表的 bug;现在这将引发ValueError(GH 15110)MultiIndex和截断的 HTML 显示 bug (GH 14882).info()显示中的 bug,当MultiIndex仅包含非字符串时,始终显示限定符 (+) (GH 15245)pd.concat()中,当输入DataFrame的MultiIndex名称中包含None时,结果DataFrame的MultiIndex名称处理不正确的 bug (GH 15787)DataFrame.sort_index()和Series.sort_index()中,na_position不适用于MultiIndex的 bug (GH 14784, GH 16604)pd.concat()在合并带有CategoricalIndex的对象时的 bug (GH 16111)使用标量和
CategoricalIndex进行索引的 bug (GH 16123)
IO#
pd.to_numeric()中浮点数和无符号整数元素被不正确转换的 bug (GH 14941, GH 15005)pd.read_fwf()中,在推断列宽时skiprows参数未被遵守的 bug (GH 11256)pd.read_csv()中,在处理前dialect参数未被验证的 bug (GH 14898)pd.read_csv()中,缺失数据在与usecols结合时被不正确处理的 bug (GH 6710)pd.read_csv()中,包含一行多列后跟少列的文件的 bug,会导致崩溃 (GH 14125)pd.read_csv()的 C 引擎中,usecols与parse_dates结合时索引不正确的 bug (GH 14792)pd.read_csv()中,当指定多行标题时parse_dates的 bug (GH 15376)pd.read_csv()中,float_precision='round_trip'导致文本条目解析时发生段错误的 bug (GH 15140)pd.read_csv()中,指定索引且未指定 null 值时的 bug (GH 15835)pd.read_csv()中,某些无效文件对象导致 Python 解释器崩溃的 bug (GH 15337)pd.read_csv()中,允许nrows和chunksize的无效值的 bug (GH 15767)pd.read_csv()的 Python 引擎中,解析错误发生时引发无用错误消息的 bug (GH 15910)pd.read_csv()中,skipfooter参数未被正确验证的 bug (GH 15925)pd.to_csv()中,写入时间戳索引时发生数字溢出的 bug (GH 15982)pd.util.hashing.hash_pandas_object()中,分类哈希依赖于类别顺序而非仅其值的 bug。(GH 15143).to_json()中,当lines=True且内容(键或值)包含转义字符时的 bug (GH 15096).to_json()导致单字节 ascii 字符扩展为四字节 unicode 的 bug (GH 15344).to_json()的 C 引擎中,当小数部分为奇数且差值恰好为 0.5 时,未正确处理进位问题的 bug (GH 15716, GH 15864)Python 2 中
pd.read_json()的 bug,当lines=True且内容包含非 ascii unicode 字符时的 bug (GH 15132)pd.read_msgpack()中,Series分类被不正确处理的 bug (GH 14901)pd.read_msgpack()不允许加载带有CategoricalIndex类型索引的 dataframe 的 bug (GH 15487)pd.read_msgpack()反序列化CategoricalIndex时的 bug (GH 15487)DataFrame.to_records()转换带有有时区的DatetimeIndex时的 bug (GH 13937)DataFrame.to_records()在列名中包含 unicode 字符时失败的 bug (GH 11879).to_sql()写入带有数字索引名称的 DataFrame 时的 bug (GH 15404)。DataFrame.to_html()中,index=False和max_rows引发IndexError的 bug (GH 14998)pd.read_hdf()将Timestamp传递给where参数,但该参数指向非日期列时的 bug (GH 15492)DataFrame.to_stata()和StataWriter导致某些区域设置生成格式不正确文件的 bug (GH 13856)StataReader和StataWriter允许无效编码的 bug (GH 15723)Seriesrepr 在输出被截断时不显示长度的 bug (GH 15962)。
绘图#
分组/重采样/滚动#
.groupby(..).resample()在传递on=kwarg 时的 bug。(GH 15021)正确设置
Groupby.*函数的__name__和__qualname__(GH 14620)GroupBy.get_group()在分类分组器下失败的 bug (GH 15155).groupby(...).rolling(...)在指定on并使用DatetimeIndex时的 bug (GH 15130, GH 13966)分组操作中,当传递
numeric_only=False时timedelta64的 bug (GH 5724)groupby.apply()中,当并非所有值都为数字时,将objectdtypes 强制转换为数字类型的 bug (GH 14423, GH 15421, GH 15670)resample中,非字符串loffset参数在重新采样时间序列时未应用的 bug (GH 13218)DataFrame.groupby().describe()在对包含元组的Index分组时的 bug (GH 14848)groupby().nunique()在使用日期时间分组器时,桶计数不正确的 bug (GH 13453)groupby.transform()强制结果 dtypes 回归原始类型的 bug (GH 10972, GH 11444)groupby.agg()错误地本地化datetime时区的 bug (GH 15426, GH 10668, GH 13046).rolling/expanding()函数中,count()未计数np.Inf且未处理objectdtypes 的 bug (GH 12541).rolling()中,pd.Timedelta或datetime.timedelta未被接受为window参数的 bug (GH 15440)Rolling.quantile函数中,当调用分位数超出 [0, 1] 范围时导致段错误的 bug (GH 15463)DataFrame.resample().median()中,存在重复列名时的 bug (GH 14233)
稀疏#
重塑#
pd.merge_asof()中,当指定多个by时,left_index或right_index导致失败的 bug (GH 15676)pd.merge_asof()中,当指定tolerance时,left_index/right_index同时使用导致失败的 bug (GH 15135)DataFrame.pivot_table()中,当列为categorydtype 时,dropna=True未删除所有 NaN 列的 bug (GH 15193)pd.melt()中,为value_vars传入元组值导致TypeError的 bug (GH 15348)pd.pivot_table()中,当 values 参数不在列中时未引发错误的 bug (GH 14938)pd.concat()中,与空 dataframe 使用join='inner'进行连接时处理不正确的 bug (GH 15328)DataFrame.join和pd.merge中,当在索引上连接时sort=True的 bug (GH 15582)DataFrame.nsmallest和DataFrame.nlargest中,相同值导致重复行的 bug (GH 15297)pandas.pivot_table()在为margins关键字传入 unicode 输入时错误地引发UnicodeError的 bug (GH 13292)
数字#
.rank()错误地对有序类别进行排名的 bug (GH 15420).corr()和.cov()中,列和索引是同一对象的 bug (GH 14617).mode()中,如果只有一个值则未返回众数的 bug (GH 15714)pd.cut()在全零数组上使用单个 bin 的 bug (GH 15428)pd.qcut()在具有相同值的数组上使用单个分位数时的 bug (GH 15431)pandas.tools.utils.cartesian_product()在 Windows 上,大输入可能导致溢出的 bug (GH 15265).eval()中,导致多行 eval 在局部变量不在第一行时失败的 bug (GH 15342)
其他#
贡献者#
共有 204 人为此版本贡献了补丁。名字旁边带有“+”的人是首次贡献补丁。
Adam J. Stewart +
Adrian +
Ajay Saxena
Akash Tandon +
Albert Villanova del Moral +
Aleksey Bilogur +
Alexis Mignon +
Amol Kahat +
Andreas Winkler +
Andrew Kittredge +
Anthonios Partheniou
Arco Bast +
Ashish Singal +
Baurzhan Muftakhidinov +
Ben Kandel
Ben Thayer +
Ben Welsh +
Bill Chambers +
Brandon M. Burroughs
Brian +
Brian McFee +
Carlos Souza +
Chris
Chris Ham
Chris Warth
Christoph Gohlke
Christoph Paulik +
Christopher C. Aycock
Clemens Brunner +
D.S. McNeil +
DaanVanHauwermeiren +
Daniel Himmelstein
Dave Willmer
David Cook +
David Gwynne +
David Hoffman +
David Krych
Diego Fernandez +
Dimitris Spathis +
Dmitry L +
Dody Suria Wijaya +
Dominik Stanczak +
Dr-Irv
Dr. Irv +
Elliott Sales de Andrade +
Ennemoser Christoph +
Francesc Alted +
Fumito Hamamura +
Giacomo Ferroni
Graham R. Jeffries +
Greg Williams +
Guilherme Beltramini +
Guilherme Samora +
Hao Wu +
Harshit Patni +
Ilya V. Schurov +
Iván Vallés Pérez
Jackie Leng +
Jaehoon Hwang +
James Draper +
James Goppert +
James McBride +
James Santucci +
Jan Schulz
Jeff Carey
Jeff Reback
JennaVergeynst +
Jim +
Jim Crist
Joe Jevnik
Joel Nothman +
John +
John Tucker +
John W. O’Brien
John Zwinck
Jon M. Mease
Jon Mease
Jonathan Whitmore +
Jonathan de Bruin +
Joost Kranendonk +
Joris Van den Bossche
Joshua Bradt +
Julian Santander
Julien Marrec +
Jun Kim +
Justin Solinsky +
Kacawi +
Kamal Kamalaldin +
Kerby Shedden
Kernc
Keshav Ramaswamy
Kevin Sheppard
Kyle Kelley
Larry Ren
Leon Yin +
Line Pedersen +
Lorenzo Cestaro +
Luca Scarabello
Lukasz +
Mahmoud Lababidi
Mark Mandel +
Matt Roeschke
Matthew Brett
Matthew Roeschke +
Matti Picus
Maximilian Roos
Michael Charlton +
Michael Felt
Michael Lamparski +
Michiel Stock +
Mikolaj Chwalisz +
Min RK
Miroslav Šedivý +
Mykola Golubyev
Nate Yoder
Nathalie Rud +
Nicholas Ver Halen
Nick Chmura +
Nolan Nichols +
Pankaj Pandey +
Pawel Kordek
Pete Huang +
Peter +
Peter Csizsek +
Petio Petrov +
Phil Ruffwind +
Pietro Battiston
Piotr Chromiec
Prasanjit Prakash +
Rob Forgione +
Robert Bradshaw
Robin +
Rodolfo Fernandez
Roger Thomas
Rouz Azari +
Sahil Dua
Sam Foo +
Sami Salonen +
Sarah Bird +
Sarma Tangirala +
Scott Sanderson
Sebastian Bank
Sebastian Gsänger +
Shawn Heide
Shyam Saladi +
Sinhrks
Stephen Rauch +
Sébastien de Menten +
Tara Adiseshan
Thiago Serafim
Thoralf Gutierrez +
Thrasibule +
Tobias Gustafsson +
Tom Augspurger
Tong SHEN +
Tong Shen +
TrigonaMinima +
Uwe +
Wes Turner
Wiktor Tomczak +
WillAyd
Yaroslav Halchenko
Yimeng Zhang +
abaldenko +
adrian-stepien +
alexandercbooth +
atbd +
bastewart +
bmagnusson +
carlosdanielcsantos +
chaimdemulder +
chris-b1
dickreuter +
discort +
dr-leo +
dubourg
dwkenefick +
funnycrab +
gfyoung
goldenbull +
hesham.shabana@hotmail.com
jojomdt +
linebp +
manu +
manuels +
mattip +
maxalbert +
mcocdawc +
nuffe +
paul-mannino
pbreach +
sakkemo +
scls19fr
sinhrks
stijnvanhoey +
the-nose-knows +
themrmax +
tomrod +
tzinckgraf
wandersoncferreira
watercrossing +
wcwagner
xgdgsc +
yui-knk